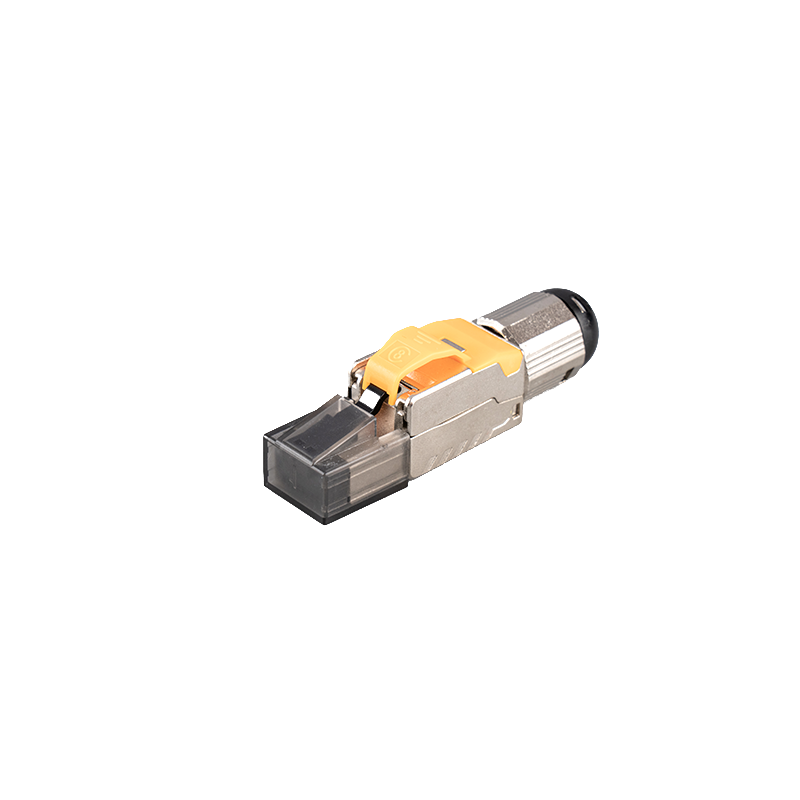
How does the Cat6 short-body module ensure the stability and security of data transmission?
The Cat6 short-body unshielded module complies with standards such as TIA/EIA-568B.2-1, EN50173, ISO/IEC 11801, etc.: These standards specify the performance requirements of network cabling systems, including key indicators such as transmission performance, impedance, and attenuation. The Cat6 short-body module complies with these standards, thereby ensuring the stability of data transmission.
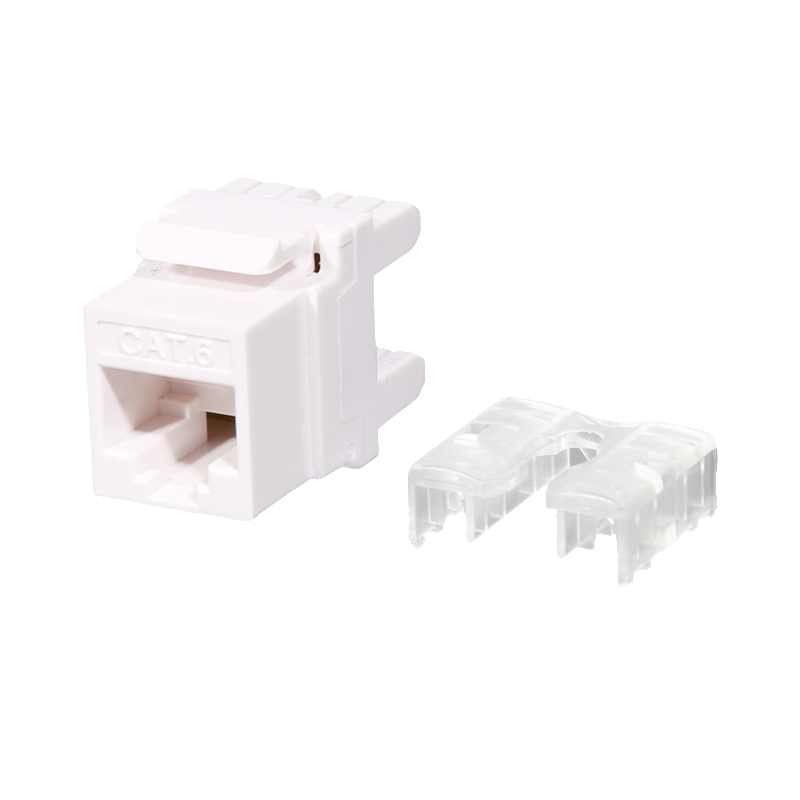
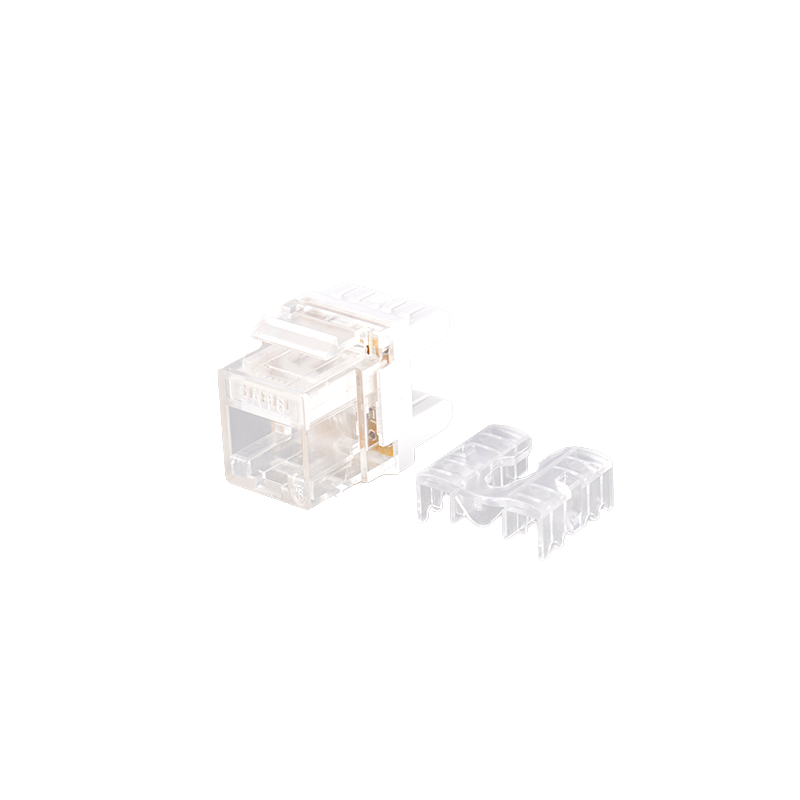
The IDC (insulation displacement connector) and contact pin materials are phosphor bronze and plated with nickel or gold. This material has good conductivity and corrosion resistance, which can ensure the integrity and stability of signal transmission. At the same time, these materials also have a high plug-in life. For example, the contact pins can withstand at least 750 plug-ins, which further improves the durability of the module. The use of cold pressing technology on the PCB board ensures a reliable connection between the PCB board and the contact pins, reducing signal attenuation or interruption caused by poor contact.
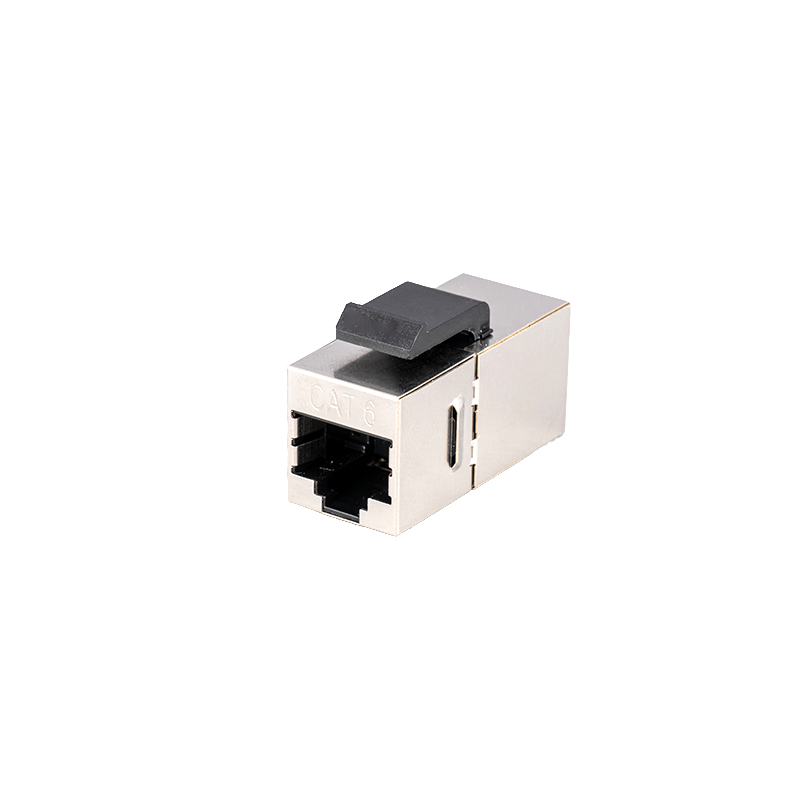
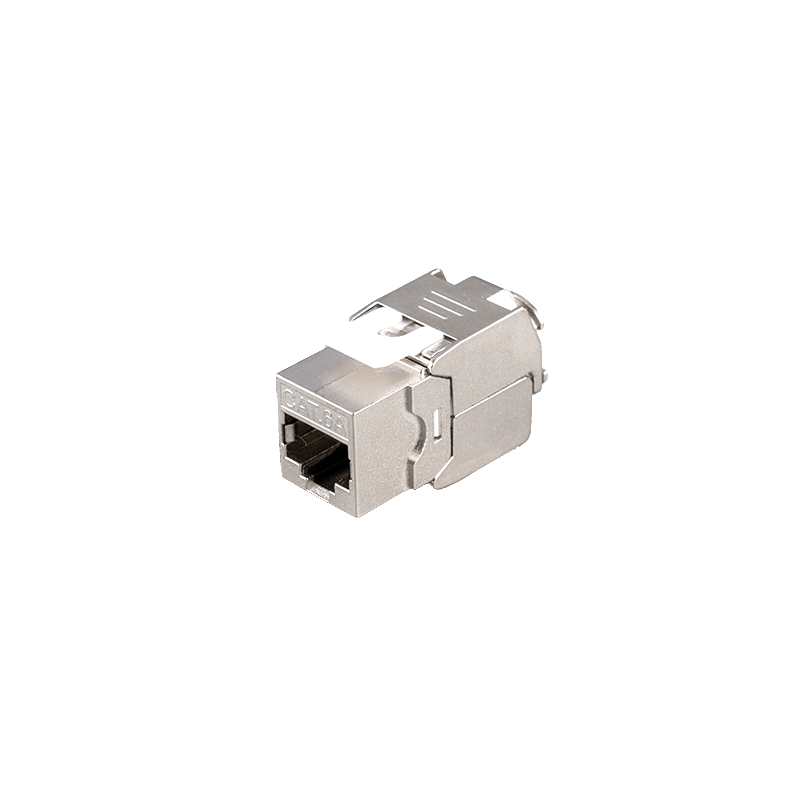
Unshielded design but meets Cat6 performance requirements: Although it is an unshielded module, its design fully considers the influence of electromagnetic interference (EMI) and radio frequency interference (RFI), and ensures the stability of data transmission in a high-noise environment by optimizing the internal structure and material selection.
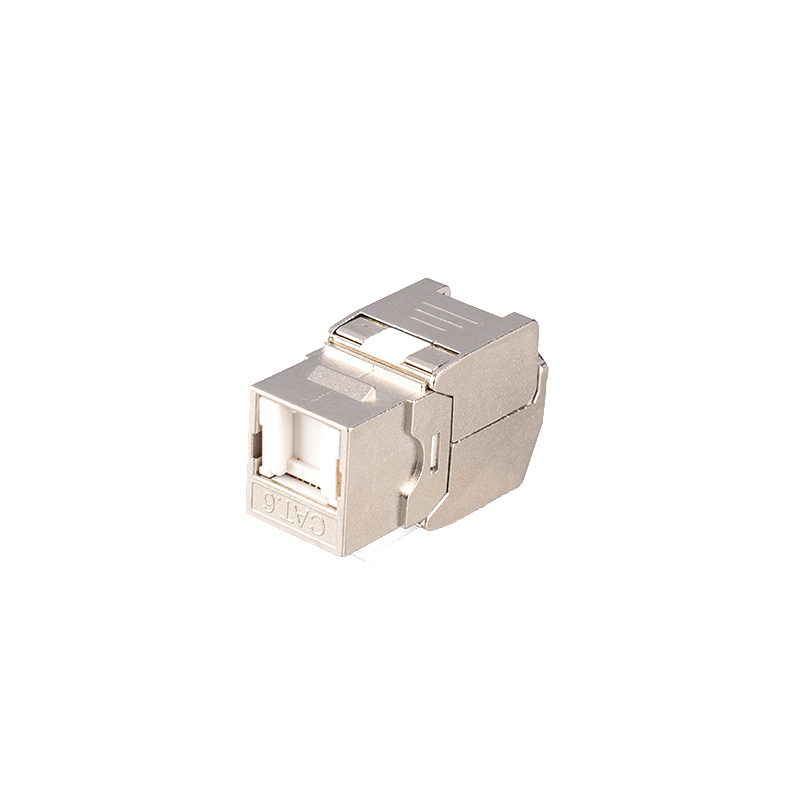
Cat6 short-body modules usually use high-quality plastic materials such as PC injection molding, which not only have excellent physical properties, but also effectively resist mechanical damage and weather effects, allowing the module to operate stably in harsh environments.
Cat6 short-body modules can support a variety of voice communication systems, Ethernet standards (such as 10Base-T, 100Base-Tx, 1000Base-Tx), and multimedia and other high-speed applications. This wide compatibility enables it to play a stable role in various network environments.
The 180° wiring method makes the module more flexible and convenient when installing, reducing signal problems caused by improper wiring.

 英语
英语 中文简体
中文简体